TENOSYNOVITIS
What is it?
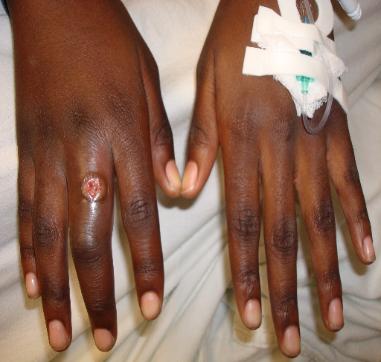
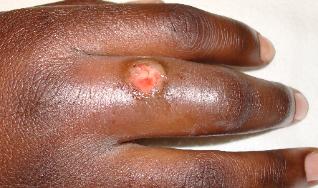
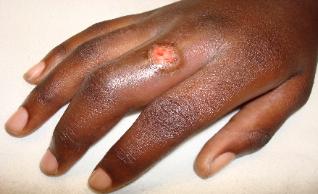
Tenosynovitis involves inflammation of the tendon and tendon sheath. Examples of tenosynovitis include de Quervain tenosynovitis of the wrist (i.e., abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendons), volar flexor tenosynovitis (i.e., trigger finger), pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis, which can be from gonococcal infections and other infectious etiologies. Infection can be introduced directly into the tendon sheaths through a skin wound (most often) or via hematogenous spread, as occurs with gonococcal tenosynovitis.
Differential Diagnosis
Joint injury
Bursitis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Bursitis
Carpal tunnel
Felon
Treatment
The goals of tenosynovitis therapy are to reduce pain and eradicate infection. NSAIDS (ibuprofen is the drug of choice) are most commonly used for the relief of mild to moderate pain. Empiric antimicrobial therapy must be comprehensive and should cover all likely pathogens in the context of the clinical setting.
Reference
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/809777-overview
What is it?
Tenosynovitis involves inflammation of the tendon and tendon sheath. Examples of tenosynovitis include de Quervain tenosynovitis of the wrist (i.e., abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendons), volar flexor tenosynovitis (i.e., trigger finger), pyogenic flexor tenosynovitis, which can be from gonococcal infections and other infectious etiologies. Infection can be introduced directly into the tendon sheaths through a skin wound (most often) or via hematogenous spread, as occurs with gonococcal tenosynovitis.
Differential Diagnosis
Joint injury
Bursitis
Rheumatoid arthritis
Bursitis
Carpal tunnel
Felon
Treatment
The goals of tenosynovitis therapy are to reduce pain and eradicate infection. NSAIDS (ibuprofen is the drug of choice) are most commonly used for the relief of mild to moderate pain. Empiric antimicrobial therapy must be comprehensive and should cover all likely pathogens in the context of the clinical setting.
Reference
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/809777-overview