DIAPER DERMATITIS
What is it?
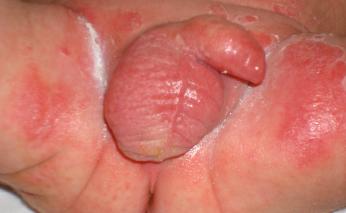
Diaper dermatitis is caused by overhydration of the skin, maceration, prolonged contact with urine and feces, retained diaper soaps, and topical preparations; it is a prototypical example of irritant contact dermatitis. Signs and symptoms are restricted in most individuals to the area covered by diapers.
Candida albicans has been identified as another contributing factor to diaper dermatitis; infection often occurs after 48-72 hours of active eruption. It is isolated from the perineal area in as many as 92% of children with diaper dermatitis. Other microbial agents have been isolated less frequently, perhaps more as a result of secondary infections.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is usually made clinically. Confirmation of candida dermatitis can be established by potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation or culture. Patients with diaper dermatitis present with an erythematous scaly diaper area often with papulovesicular or bullous lesions, fissures, and erosions. The eruption may be patchy or confluent, affecting the abdomen from the umbilicus down to the thighs and encompassing the genitalia, perineum, and buttocks. Genitocrural folds are spared in irritant dermatitis, but often involved in primary candida dermatitis.
Differential Diagnosis
Atopic dermatitis
Contact dermatitis
Biotin deficiency
Syphilis
Scabies
Varicella
HSV infection
Treatment
Parent education is very important. The area must be washed with warm water and a mild soap, and a bland topical barrier agent such as zinc oxide ointment placed to skin after each diaper change. Diapers must be changed frequently. If candidiasis is suspected or proven by potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation or culture, an antifungal agent effective against yeast, such as nystatin cream, is indicated after each diaper change. If significant inflammation is obvious, hydrocortisone 1% can be used for the first 1-2 days. Avoid higher strength topical steroids found in combination products such as clotrimazole/betamethasone and nystatin/triamcinolone.
References:
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/911985-overview
http://www.uptodate.com/online/content/search.do?search=candida+dermatitis&source=USER_INPUT&searchOffset=&_NEXTITEM=submitType&_E
What is it?
Diaper dermatitis is caused by overhydration of the skin, maceration, prolonged contact with urine and feces, retained diaper soaps, and topical preparations; it is a prototypical example of irritant contact dermatitis. Signs and symptoms are restricted in most individuals to the area covered by diapers.
Candida albicans has been identified as another contributing factor to diaper dermatitis; infection often occurs after 48-72 hours of active eruption. It is isolated from the perineal area in as many as 92% of children with diaper dermatitis. Other microbial agents have been isolated less frequently, perhaps more as a result of secondary infections.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is usually made clinically. Confirmation of candida dermatitis can be established by potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation or culture. Patients with diaper dermatitis present with an erythematous scaly diaper area often with papulovesicular or bullous lesions, fissures, and erosions. The eruption may be patchy or confluent, affecting the abdomen from the umbilicus down to the thighs and encompassing the genitalia, perineum, and buttocks. Genitocrural folds are spared in irritant dermatitis, but often involved in primary candida dermatitis.
Differential Diagnosis
Atopic dermatitis
Contact dermatitis
Biotin deficiency
Syphilis
Scabies
Varicella
HSV infection
Treatment
Parent education is very important. The area must be washed with warm water and a mild soap, and a bland topical barrier agent such as zinc oxide ointment placed to skin after each diaper change. Diapers must be changed frequently. If candidiasis is suspected or proven by potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation or culture, an antifungal agent effective against yeast, such as nystatin cream, is indicated after each diaper change. If significant inflammation is obvious, hydrocortisone 1% can be used for the first 1-2 days. Avoid higher strength topical steroids found in combination products such as clotrimazole/betamethasone and nystatin/triamcinolone.
References:
http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/911985-overview
http://www.uptodate.com/online/content/search.do?search=candida+dermatitis&source=USER_INPUT&searchOffset=&_NEXTITEM=submitType&_E